什么叫Chain,从字面意思理解,Chain是一个链,我们可以通过Chain来链接LangChain的各个组件和功能-模型之间彼此链接,或模型与其他组件链接。
 这种将多个组件相互链接,组合成一个链的想法简单但很强大。它简化了复杂应用程序的实现,并使之更加模块化,能够创建出单一的、连贯的应用程序,从而使调试、维护和改进应用程序变得容易。
这种将多个组件相互链接,组合成一个链的想法简单但很强大。它简化了复杂应用程序的实现,并使之更加模块化,能够创建出单一的、连贯的应用程序,从而使调试、维护和改进应用程序变得容易。
我们可以简单的把Chain理解为通过设计好的一些链路去调用大模型,从而获取我们想要的结果。下面是一个例子:
首先我们让大模型扮演产品经理,给出小说推荐网站的产品设计。
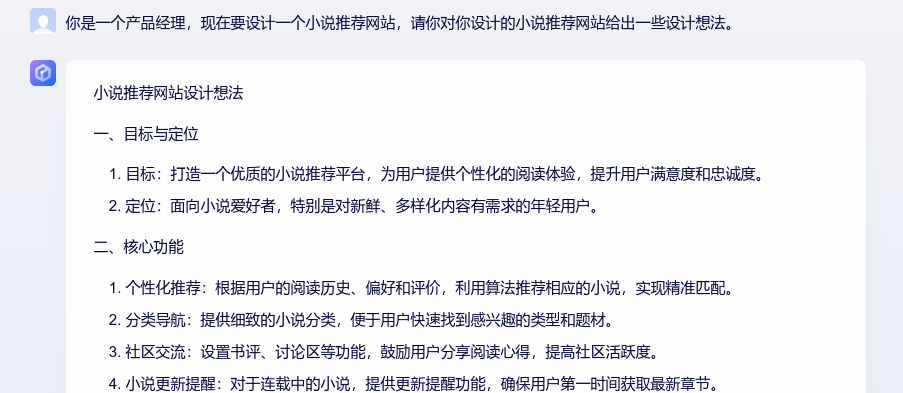
有了产品设计后,由架构师进行初步的架构设计


现在架构设计也有了,来个程序员写SQL:

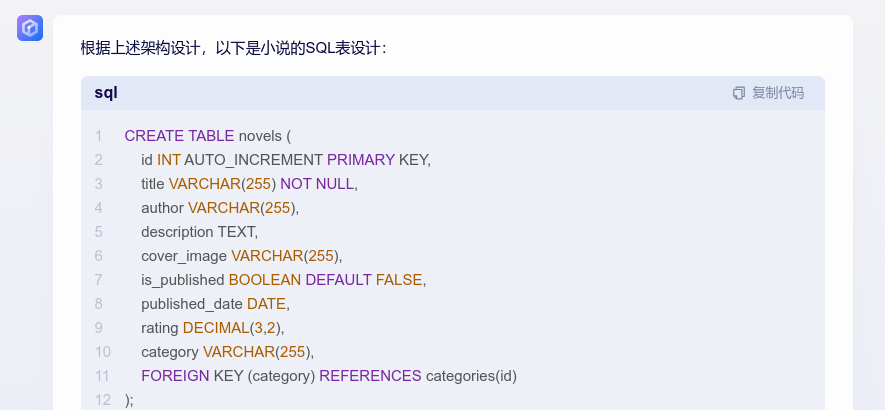 那,上面的这种promot链,我们用langchain怎么实现呢?
那,上面的这种promot链,我们用langchain怎么实现呢?
使用langchain实现
Sequential Chain
首先,导入所有需要的库
# 设置OpenAI API密钥
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = '你的OpenAI API Key'
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import SequentialChain
添加第一个LLMChain,生成小说网站的产品设计。LLMChain可以看作是链条的一个环节
# 这是第一个LLMChain,用于生成鲜花的介绍,输入为花的名称和种类
llm = OpenAI(temperature=.7)
template = """
你是一个产品经理,请你对{product}给出一个设计想法。"""
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["product"], template=template)
introduction_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt_template, output_key="introduction")
添加第二个LLMChain,根据产品设计生成软件架构
# 这是第二个LLMChain,用于根据鲜花的介绍写出鲜花的评论
llm = OpenAI(temperature=.7)
template = """
你是一位软件架构师。给定一个{product}的设计,你需要给出产品软件架构说明和技术栈选型。
产品设计:
{introduction}
软件架构说明:"""
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["product", "introduction"], template=template)
review_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt_template, output_key="framwork")
第三个Chain,根据产品架构生成SQL语句
# 这是第三个LLMChain,用于根据鲜花的介绍和评论写出一篇自媒体的文案
template = """
你是一个软件工程师,给定一个{product}的软件架构,请你给出其中主要的数据库表的SQL语句
软件架构:
{framwork}
SQL语句:
"""
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["product", "framwork"], template=template)
social_post_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt_template, output_key="sql_text")
最后,添加SequentialChain,把前面三个链串起来。
overall_chain = SequentialChain(
chains=[introduction_chain, review_chain, social_post_chain],
input_variables=["product"],
output_variables=["introduction","framework","sql_text"],
verbose=True)
# 运行链,并打印结果
result = overall_chain({"product":"小说推荐网站"})
print(result)
输出:
{
"product": "小说推荐网站",
"introduction": "作为一个产品经理,我会考虑以下设计想法来提高小说推荐网站的用户体验和吸引力:\n\n1. 个性化推荐:基于用户的阅读历史、喜好和评分等信息,为用户推荐个性化的小说列表。可以通过机器学习算法和数据分析来实现。\n\n2. 社交互动:为用户提供社交功能,让用户可以在网站上与其他读者交流、分享和评论小说。这样可以增加用户的参与度和忠诚度。\n\n3. 多维度分类:除了按照类型、作者、出版社等传统分类方式,还可以增加按照情节、主题、人物等多维度分类方式,让用户更容易找到自己喜欢的小说。\n\n4. 优质内容推荐:为用户推荐优质的小说内容,可以通过与出版社、作家等合作,或者通过专业编辑团队筛选出优秀的小说。\n\n5. 移动端适配:随着移动设备的普及,小说推荐网站需要适配移动端,提供更好的用户体验和便捷的阅读方式。\n\n6. 付费服务:为用户提供付费服务,例如VIP会员、广告免费等,以增加网站的收入和用户忠诚度。\n\n以上是我对小说推荐网站的设计想法,希望能够对您有所帮助。",
"framework": "基于以上产品设计,我建议采用微服务架构,将不同的功能模块拆分成独立的服务,以提高系统的可扩展性和可维护性。具体架构如下:\n\n1. 用户服务:负责用户注册、登录、个人信息管理等功能。\n\n2. 推荐服务:基于用户的阅读历史、喜好和评分等信息,为用户推荐个性化的小说列表。\n\n3. 社交服务:负责用户之间的交流、分享和评论等社交功能。\n\n4. 分类服务:负责小说的多维度分类和搜索功能。\n\n5. 内容服务:负责小说的内容管理和优质内容推荐。\n\n6. 支付服务:负责用户付费服务的管理和支付功能。\n\n7. 移动端服务:负责移动端的适配和提供更好的用户体验和便捷的阅读方式。\n\n技术栈选型:\n\n1. 后端框架:Spring Boot、Spring Cloud\n\n2. 数据库:MySQL、Redis\n\n3. 消息队列:Kafka\n\n4. 搜索引擎:Elasticsearch\n\n5. 缓存:Redis\n\n6. 前端框架:React、Ant Design\n\n7. 移动端框架:React Native\n\n8. 机器学习算法:TensorFlow、Scikit-learn\n\n9. 云服务:AWS、阿里云\n\n以上是我对小说推荐网站的软件架构说明和技术栈选型建议,希望能够对您有所帮助。",
"sql_text": "以下是主要的数据库表的SQL语句:\n\n1. 用户服务:\n\nCREATE TABLE users (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,\n password VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,\n email VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,\n phone VARCHAR(20),\n avatar VARCHAR(100),\n created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP\n);\n\n2. 推荐服务:\n\nCREATE TABLE user_read_history (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n user_id INT NOT NULL,\n book_id INT NOT NULL,\n read_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id),\n FOREIGN KEY (book_id) REFERENCES books(id)\n);\n\nCREATE TABLE user_rating (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n user_id INT NOT NULL,\n book_id INT NOT NULL,\n rating INT NOT NULL,\n FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id),\n FOREIGN KEY (book_id) REFERENCES books(id)\n);\n\n3. 社交服务:\n\nCREATE TABLE comments (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n user_id INT NOT NULL,\n book_id INT NOT NULL,\n content TEXT NOT NULL,\n created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id),\n FOREIGN KEY (book_id) REFERENCES books(id)\n);\n\n4. 分类服务:\n\nCREATE TABLE categories (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,\n parent_id INT,\n created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n FOREIGN KEY (parent_id) REFERENCES categories(id)\n);\n\nCREATE TABLE book_category (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n book_id INT NOT NULL,\n category_id INT NOT NULL,\n FOREIGN KEY (book_id) REFERENCES books(id),\n FOREIGN KEY (category_id) REFERENCES categories(id)\n);\n\n5. 内容服务:\n\nCREATE TABLE books (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n title VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,\n author VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,\n description TEXT NOT NULL,\n cover VARCHAR(100),\n created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP\n);\n\n6. 支付服务:\n\nCREATE TABLE orders (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n user_id INT NOT NULL,\n book_id INT NOT NULL,\n amount DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,\n status INT NOT NULL,\n created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id),\n FOREIGN KEY (book_id) REFERENCES books(id)\n);\n\n7. 移动端服务:\n\nCREATE TABLE devices (\n id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,\n user_id INT NOT NULL,\n device_token VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,\n device_type INT NOT NULL,\n created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,\n FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id)\n);"
}
langchain还提供了许多其他类型的链:https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/chains
Router Chain
Sequential Chain只是根据设计好的思维链路进行思考,但有时我们会面临抉择,在收到不同的任务时让不同的角色去完成。例如,现在我们有两个角色:软件架构师,软件工程师,我们需要根据问题的内容决定让谁去回答问题。首先构建两个提示信息的模板:
# 构建两个场景的模板
frame_template = """你是一个经验丰富的软件架构师,擅长解答关于软件架构,技术选型的问题。
下面是需要你来回答的问题:
{input}"""
engineer_template = """你是一位软件工程师,擅长解决技术细节,代码编写的问题。
下面是需要你来回答的问题:
{input}"""
# 构建提示信息
prompt_infos = [
{
"key": "framework",
"description": "擅长解答关于软件架构,技术选型的问题",
"template": frame_template,
},
{
"key": "engineer",
"description": "擅长解决技术细节,代码编写的问题",
"template": engineer_template,
}]
初始化语言模型
# 初始化语言模型
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = '你的OpenAI Key'
llm = OpenAI()
构建目标链
# 构建目标链
from langchain.chains.llm import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
chain_map = {}
for info in prompt_infos:
prompt = PromptTemplate(template=info['template'],
input_variables=["input"])
print("目标提示:\n",prompt)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt,verbose=True)
chain_map[info["key"]] = chain
目标链长这个样子:
目标提示:
input_variables=['input'] output_parser=None partial_variables={} template='你是一个经验丰富的软件架构师,擅长解答关于软件架构,技术选型的问题。\n 下面是需要你来回答的问题:\n {input}' template_format='f-string' validate_template=True
目标提示:
input_variables=['input'] output_parser=None partial_variables={} template='你是一位软件工程师,擅长解决技术细节,代码编写的问题。\n 下面是需要你来回答的问题:\n {input}' template_format='f-string' validate_template=True
构建路由链:
# 构建路由链
from langchain.chains.router.llm_router import LLMRouterChain, RouterOutputParser
from langchain.chains.router.multi_prompt_prompt import MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE as RounterTemplate
destinations = [f"{p['key']}: {p['description']}" for p in prompt_infos]
router_template = RounterTemplate.format(destinations="\n".join(destinations))
print("路由模板:\n",router_template)
router_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=router_template,
input_variables=["input"],
output_parser=RouterOutputParser(),)
print("路由提示:\n",router_prompt)
router_chain = LLMRouterChain.from_llm(llm,
router_prompt,
verbose=True)
路由模板的样子:
路由模板:
Given a raw text input to a language model select the model prompt best suited for the input. You will be given the names of the available prompts and a description of what the prompt is best suited for. You may also revise the original input if you think that revising it will ultimately lead to a better response from the language model.
<< FORMATTING >>
Return a markdown code snippet with a JSON object formatted to look like:
```json
{{
"destination": string \ name of the prompt to use or "DEFAULT"
"next_inputs": string \ a potentially modified version of the original input
}}
REMEMBER: “destination” MUST be one of the candidate prompt names specified below OR it can be “DEFAULT” if the input is not well suited for any of the candidate prompts. REMEMBER: “next_inputs” can just be the original input if you don’t think any modifications are needed.
« CANDIDATE PROMPTS » framework: 擅长解答关于软件架构,技术选型的问题 engineer: 擅长解决技术细节,代码编写的问题
« INPUT » {input}
« OUTPUT »
路由提示:
input_variables=[‘input’] output_parser=RouterOutputParser(default_destination=‘DEFAULT’, next_inputs_type=<class ‘str’>, next_inputs_inner_key=‘input’) partial_variables={} template=‘Given a raw text input to a language model select the model prompt best suited for the input. You will be given the names of the available prompts and a description of what the prompt is best suited for. You may also revise the original input if you think that revising it will ultimately lead to a better response from the language model.\n\n« FORMATTING »\nReturn a markdown code snippet with a JSON object formatted to look like:\njson\n{{\n "destination": string \\ name of the prompt to use or "DEFAULT"\n "next_inputs": string \\ a potentially modified version of the original input\n}}\n\n\nREMEMBER: “destination” MUST be one of the candidate prompt names specified below OR it can be “DEFAULT” if the input is not well suited for any of the candidate prompts.\nREMEMBER: “next_inputs” can just be the original input if you don't think any modifications are needed.\n\n« CANDIDATE PROMPTS »\nframework: 擅长解答关于软件架构,技术选型的问题\nengineer: 擅长解决技术细节,代码编写的问题\n\n« INPUT »\n{input}\n\n« OUTPUT »\n’ template_format=‘f-string’ validate_template=True
构建默认链,除了处理目标链和路由链之外,我们还需要准备一个默认链。如果路由链没有找到适合的链,那么,就以默认链进行处理。
```python
# 构建默认链
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
default_chain = ConversationChain(llm=llm,
output_key="text",
verbose=True)
最后,我们使用 MultiPromptChain 类把前几个链整合在一起,实现路由功能。这个 MultiPromptChain 类是一个多路选择链,它使用一个 LLM 路由器链在多个提示之间进行选择。MultiPromptChain 中有三个关键元素。
- router_chain(类型 RouterChain):这是用于决定目标链和其输入的链。当给定某个输入时,这个 router_chain 决定哪一个 destination_chain 应该被选中,以及传给它的具体输入是什么。
- destination_chains(类型 Mapping[str, LLMChain]):这是一个映射,将名称映射到可以将输入路由到的候选链。例如,你可能有多种处理文本输入的方法(或“链”),每种方法针对特定类型的问题。destination_chains 可以是这样一个字典:{‘weather’: weather_chain, ‘news’: news_chain}。在这里,weather_chain 可能专门处理与天气相关的问题,而 news_chain 处理与新闻相关的问题。
- default_chain(类型 LLMChain):当 router_chain 无法将输入映射到 destination_chains 中的任何一个链时,LLMChain 将使用此默认链。这是一个备选方案,确保即使路由器不能决定正确的链,也总有一个链可以处理输入。
它的工作流程如下:
- 输入首先传递给 router_chain。
- router_chain 根据某些标准或逻辑决定应该使用哪一个 destination_chain。
- 输入随后被路由到选定的 destination_chain,该链进行处理并返回结果。如果 router_chain 不能决定正确的 destination_chain,则输入会被传递给 default_chain。
- 这样,MultiPromptChain 就为我们提供了一个在多个处理链之间动态路由输入的机制,以得到最相关或最优的输出。
# 构建多提示链
from langchain.chains.router import MultiPromptChain
chain = MultiPromptChain(
router_chain=router_chain,
destination_chains=chain_map,
default_chain=default_chain,
verbose=True)
开始运行吧:
print(chain.run("博客网站应该如何设计"))
输出如下:
> Entering new chain...
> Entering new chain...
> Finished chain.
framework: {'input': '博客网站应该如何设计'}
> Entering new chain...
Prompt after formatting:
你是一个经验丰富的软件架构师,擅长解答关于软件架构,技术选型的问题。
下面是需要你来回答的问题:
博客网站应该如何设计
> Finished chain.
> Finished chain.
博客网站的设计应该考虑以下几个方面:
1. 用户体验:博客网站应该易于使用,用户可以轻松地找到他们感兴趣的内容。网站应该具有良好的导航和搜索功能,以便用户可以快速找到他们需要的信息。
2. 响应式设计:博客网站应该能够适应不同的设备和屏幕大小,包括桌面电脑、平板电脑和手机等。这样可以确保用户在任何设备上都能够方便地访问网站。
。。。。(略)