大模型可以回答你的任何问题,但有时我们需要将大模型的回复进行格式化解析以便进行后续的处理,此时就需要我们使用一些特殊的技巧提示大模型:你应该如此如此,这般这般返回一个简单的例子(文心一言):

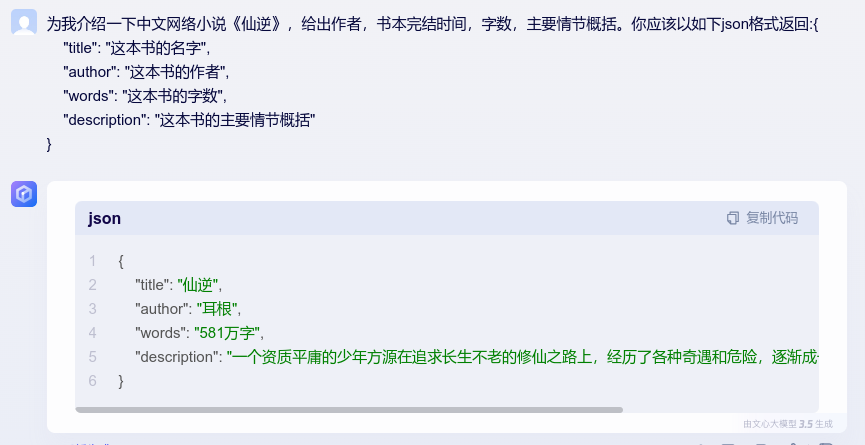 可以看到,我们在prompt中告诉大模型,你应该以如下json格式返回,大模型按照我们的要求,切实返回了我们要求的json格式。这样,我们就可以把大模型的输出进行解析,大模型的输出,不再是无法解析的数据。langchain为我们提供了一系列工具来为prompt添加输出格式指令,解析输出,重试机制等等。
可以看到,我们在prompt中告诉大模型,你应该以如下json格式返回,大模型按照我们的要求,切实返回了我们要求的json格式。这样,我们就可以把大模型的输出进行解析,大模型的输出,不再是无法解析的数据。langchain为我们提供了一系列工具来为prompt添加输出格式指令,解析输出,重试机制等等。
使用LangChain工具
PydanticOutputParser(json输出解析)
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser, OutputFixingParser
class FlowerDescription(BaseModel):
title: str = Field(description="这本书的标题")
author: int = Field(description="这本书的作者")
words: str = Field(description="这本书的字数")
description: str = Field(description="这本书的主要情节")
# 定义输出解析器
output_parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=FlowerDescription)
# 获取输出格式指示
format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
print(format_instructions)
The output should be formatted as a JSON instance that conforms to the JSON schema below.
As an example, for the schema {"properties": {"foo": {"title": "Foo", "description": "a list of strings", "type": "array", "items": {"type": "string"}}}, "required": ["foo"]}}
the object {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]} is a well-formatted instance of the schema. The object {"properties": {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]}} is not well-formatted.
Here is the output schema:
{“properties”: {“title”: {“title”: “Title”, “description”: “\u8fd9\u672c\u4e66\u7684\u6807\u9898”, “type”: “string”}, “author”: {“title”: “Author”, “description”: “\u8fd9\u672c\u4e66\u7684\u4f5c\u8005”, “type”: “integer”}, “words”: {“title”: “Words”, “description”: “\u8fd9\u672c\u4e66\u7684\u5b57\u6570”, “type”: “string”}, “description”: {“title”: “Description”, “description”: “\u8fd9\u672c\u4e66\u7684\u4e3b\u8981\u60c5\u8282”, “type”: “string”}}, “required”: [“title”, “author”, “words”, “description”]}
定义了解析器之后,我们需要将其添加到prompt中
from langchain import PromptTemplate
prompt_template = '''为我介绍一下中文网络小说《仙逆》,给出作者,书本完结时间,字数,主要情节概括。
{format_instructions}''' # 这里添加了一个变量format_instructions
# 根据模板创建提示,同时在提示中加入输出解析器的说明
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(prompt_template,
partial_variables={"format_instructions": format_instructions})
input = prompt.format()
output = llm.predict(input)
print(output)
输出:
{
"title": "仙逆",
"author": "耳根",
"words": "580万字",
"description": "《仙逆》是耳根所著的一部玄幻小说,于2012年完结。小说讲述了一个少年从凡人到成为仙界巨擘的传奇故事。主人公方源在修仙的道路上历经艰辛,不断突破自我,最终成为了仙界的强者。小说情节曲折离奇,人物形象鲜明,被誉为中国网络小说的经典之作。"
}
确实得到了格式化输出(虽然主角错了。。),现在我们把输出解析到刚才定义的结构上
parsed_output = output_parser.parse(output)
parsed_output_dict = parsed_output.dict() # 将Pydantic格式转换为字典
print(parsed_output_dict)
错误回复的修复
一般情况下,大模型能够给出符合要求的回复,但有时抽风也会出问题,这时候就需要我们采取一定的措施来对大模型的输出进行修复。
OutputFixingParser
在 OutputFixingParser 内部,调用了原有的 PydanticOutputParser,如果成功,就返回;如果失败,它会将格式错误的输出以及格式化的指令传递给大模型,并要求 LLM 进行相关的修复。
# 定义一个模板字符串,这个模板将用于生成提问
template = """Based on the user question, provide an Action and Action Input for what step should be taken.
{format_instructions}
Question: {query}
Response:"""
# 定义一个Pydantic数据格式,它描述了一个"行动"类及其属性
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Action(BaseModel):
action: str = Field(description="action to take")
action_input: str = Field(description="input to the action")
# 使用Pydantic格式Action来初始化一个输出解析器
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Action)
# 定义一个提示模板,它将用于向模型提问
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="Answer the user query.\n{format_instructions}\n{query}\n",
input_variables=["query"],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()},
)
prompt_value = prompt.format_prompt(query="What are the colors of Orchid?")
# 定义一个错误格式的字符串
bad_response = '{"action": "search"}'
from langchain.output_parsers import OutputFixingParser
fix_parser = OutputFixingParser.from_llm(parser=parser, llm=llm)
parse_result = fix_parser.parse(bad_response)
print('OutputFixingParser的parse结果:', parse_result)
RetryWithErrorOutputParser
OutputFixingParser 不错,但它只能做简单的格式修复。如果出错的不只是格式,比如,输出根本不完整,有缺失内容,那么仅仅根据输出和格式本身,是无法修复它的。此时,通过实现输出解析器中 parse_with_prompt 方法,LangChain 提供的重试解析器可以帮助我们利用大模型的推理能力根据原始提示找回相关信息。
# 定义一个模板字符串,这个模板将用于生成提问
template = """Based on the user question, provide an Action and Action Input for what step should be taken.
{format_instructions}
Question: {query}
Response:"""
# 定义一个Pydantic数据格式,它描述了一个"行动"类及其属性
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Action(BaseModel):
action: str = Field(description="action to take")
action_input: str = Field(description="input to the action")
# 使用Pydantic格式Action来初始化一个输出解析器
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Action)
# 定义一个提示模板,它将用于向模型提问
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="Answer the user query.\n{format_instructions}\n{query}\n",
input_variables=["query"],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()},
)
prompt_value = prompt.format_prompt(query="What are the colors of Orchid?")
# 定义一个错误格式的字符串
bad_response = '{"action": "search"}'
from langchain.output_parsers import OutputFixingParser
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
fix_parser = OutputFixingParser.from_llm(parser=parser, llm=ChatOpenAI())
parse_result = fix_parser.parse(bad_response)
print('OutputFixingParser的parse结果:',parse_result)
在选择哪种解析器时,需要考虑具体的应用场景。如果仅面临格式问题,自动修复解析器可能足够;但如果输出的完整性和准确性至关重要,那么重试解析器可能是更好的选择。
langchain中还提供了各种各样的解析器,但基本原理都与我们上面介绍的类似:https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/model_io/output_parsers/